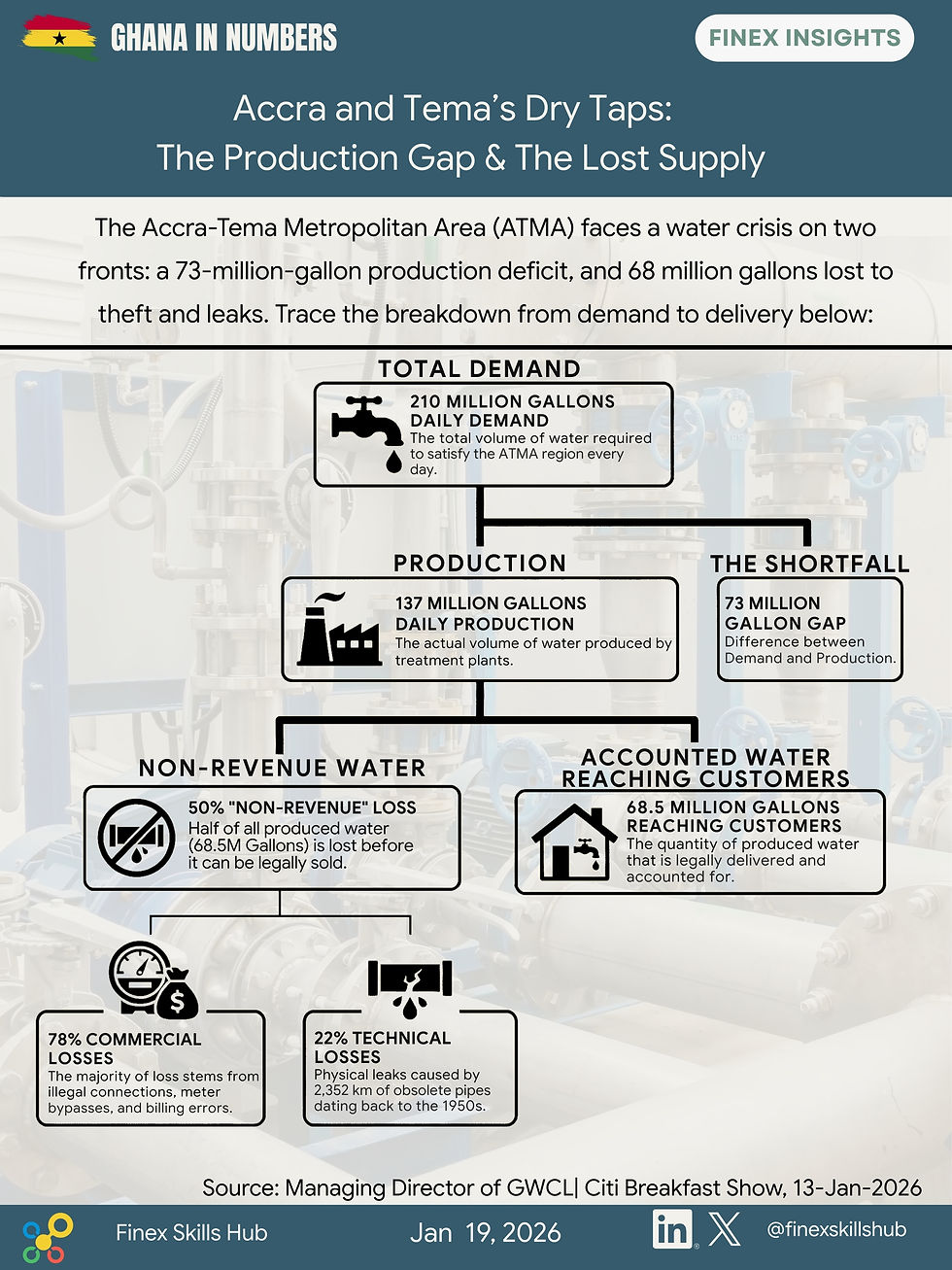
Is ECOWAS Shrinking? Exploring the Impact of the Sahel Confederation on West Africa
- bernard boateng
- Jul 12, 2024
- 3 min read
Updated: May 27, 2025
Introduction
The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) has long been a pillar of regional cooperation, economic stability, and security in West Africa. However, recent political instability and military coups have led to the suspension of several key members, including Mali, Niger, and Burkina Faso. This shift has significant implications for ECOWAS and the broader region. Additionally, the formation of the Sahel Confederation, a new alliance among these suspended states, marks a transformative moment in West African geopolitics. This article explores the current landscape of ECOWAS, the rise of the Sahel Confederation, and the potential economic and security impacts of these developments.

The Current Status of ECOWAS
As of July 2024, ECOWAS comprises 15 member states. However, the organization has faced challenges due to political upheaval in several countries. The map above illustrates the status of each member state:
Active Members: Benin, Cape Verde, Côte d'Ivoire, Ghana, Gambia, Guinea-Bissau, Liberia, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Togo
Suspended Members: Guinea
Suspended | Now Part of the Sahel Confederation: Mali, Niger, Burkina Faso
The Formation of the Sahel Confederation
The Sahel Confederation is a newly established alliance formed by Mali, Niger, and Burkina Faso. These countries, suspended from ECOWAS due to military coups, have sought to strengthen their political and security cooperation through this new entity. The Sahel Confederation aims to address common challenges such as terrorism, economic development, and regional stability.
Recent Developments
Political Motivations: The Sahel Confederation was formed as a response to perceived marginalization within ECOWAS and a desire for greater autonomy in addressing regional issues.
Security Cooperation: One of the primary goals of the Sahel Confederation is to enhance collaborative efforts in combating terrorism and insurgency in the Sahel region. The new alliance aims to create a unified front against extremist groups operating across their borders.
Economic Integration: The Sahel Confederation seeks to promote economic cooperation and development projects that cater specifically to the needs of its member states, which are often different from those of coastal West African nations.
Implications of ECOWAS Member Statuses
Active Members (Green)
Economic Stability: Active members benefit from and contribute to the economic cooperation and trade agreements within ECOWAS, fostering regional development and integration.
Security Collaboration: Participation in regional security initiatives enhances collective efforts to combat terrorism and organized crime.
Suspended Members (Brown)
Economic Disruption: Suspension leads to reduced access to ECOWAS economic resources and markets, potentially causing economic instability and hindering development projects.
Security Challenges: Suspension can weaken regional security cooperation, making it harder to address transnational threats and internal conflicts.
Suspended | Now Part of the Sahel Confederation (Gray)
Shift in Alliances: The shift to the Sahel Confederation reflects changing regional dynamics, possibly impacting ECOWAS’s influence and cohesion.
Economic and Security Realignment: The new alignment might lead to different economic partnerships and security strategies, affecting regional stability and cooperation.
The Economic and Security Impact of the Sahel Confederation
Economic Impact
The departure of Mali, Niger, and Burkina Faso from ECOWAS to form the Sahel Confederation could lead to significant economic disruptions:
Trade Disruptions: The fragmentation of the common market could hinder regional trade, affecting supply chains and economic growth.
Investment Uncertainty: Political instability and the realignment of alliances might deter foreign investment, crucial for economic development in these countries.
Security Impact
The Sahel region has been a hotspot for terrorism and insurgency. The formation of the Sahel Confederation aims to bolster security efforts, but it also presents challenges:
Counterterrorism Coordination: While the Sahel Confederation enhances local coordination, it may complicate broader regional security efforts that previously involved ECOWAS.
Border Security: The new alliance must navigate complex border security issues, balancing cooperation with neighboring states and internal security needs.
Conclusion
The evolving dynamics within ECOWAS and the formation of the Sahel Confederation highlight significant shifts in West African geopolitics. As ECOWAS navigates the suspension of key members and the emergence of a new regional alliance, the implications for economic stability and security are profound. Understanding these developments is crucial for policymakers, investors, and stakeholders engaged in West Africa's future.
Bernard Obeng Boateng
Lead Trainer - Finex Skills Hub
+233244782356


Comments